acetabular labral tear special tests accuracy trial|acetabular labral tear management : department Store The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); . Un autoclave es un dispositivo que se emplea para la esterilización de diferentes sustancias u objetos. Se trata de un equipo que, según sus características, puede recurrir a la radiación, la temperatura alta o el vapor .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Quanto Tempo Demora a esterilização de autoclaves? Práticas, as autoclaves realizam a esterilização de equipamentos da forma mais segura e rápida possível. A duração .
The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); .
A PT, an OS, and two ORs independently performed history and examinations with the emp. A more recent study in those with acetabular labral tear has shown that conservative management over the course of 1 year with corticosteroid injection, activity .
The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only .
A more recent study in those with acetabular labral tear has shown that conservative management over the course of 1 year with corticosteroid injection, activity modification, and physical therapy led to improved functional outcomes, and 71% of patients were satisfied with nonsurgical treatment. The purpose of this study was to determine (1) the diagnostic accuracy of MRI and MRA for the detection of ALT, (2) whether 1.5 T or 3.0 T is all acceptable, by conducting a meta-analysis of the literature regarding the diagnostic performance of MRI/MRA.We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An acetabular labral tear is a diagnostic challenge. Various clinical tests have been described, but little is known about their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity.Prevalence of acetabular labral tears in patients presenting with hip or groin pain has been reported to be between 22% (Narvani et al., 2003) and 55% (McCarthy et al., 2001).
There are few well-studied clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip labral tears. As the differential diagnosis for hip pain is broad, accurate clinical examination is important in guiding advanced imaging and identifying patients who may benefit from surgical management. Purpose:A PT, an OS, and two ORs independently performed history and examinations with the emphasis of diagnosis on the results of six special tests. Results: Thirty-two of 37 individuals (86%) had labral tears to the hip at arthroscopy.
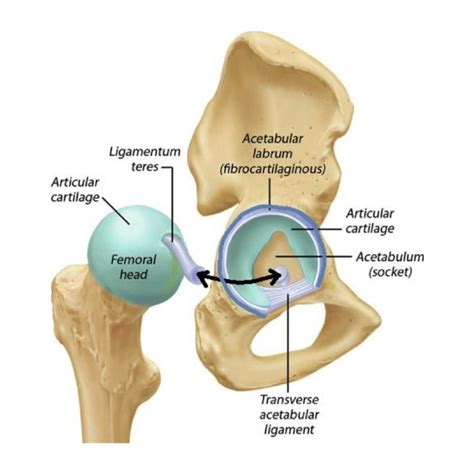
Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging.
treatment for acetabular tear
labral tear diagnosis
wpi glass pipette
Specific provocative tests for acetabular labral tears have been described in the literature, all of which involve stressing or loading the hip joint in rotation. However, no single test has been identified as having a significant positive predictive value in .Future studies calculating accuracy of Arlington and Twist tests in the hands of other clinicians will help to validate our findings. •The combination of these 3 tests will be useful to guide appropriate use and interpretation of advanced imaging. References. 1.The meta-analysis demonstrated that flexion-adduction-internal rotation (pooled SN ranging from 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.97) to 0.99 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.00); DOR 5.71 (95% CI 0.84 to 38.86) to 7.82 (95% CI 1.06 to 57.84)) and flexion-internal rotation (pooled SN 0.96 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99); DOR 8.36 (95% CI 0.41 to 171.3) tests possess only .
A more recent study in those with acetabular labral tear has shown that conservative management over the course of 1 year with corticosteroid injection, activity modification, and physical therapy led to improved functional outcomes, and 71% of patients were satisfied with nonsurgical treatment. The purpose of this study was to determine (1) the diagnostic accuracy of MRI and MRA for the detection of ALT, (2) whether 1.5 T or 3.0 T is all acceptable, by conducting a meta-analysis of the literature regarding the diagnostic performance of MRI/MRA.We investigated the diagnostic validity of clinical tests . Background and purpose An acetabular labral tear is a diagnostic challenge. Various clinical tests have been described, but little is known about their diagnostic sensitivity and specificity.
Prevalence of acetabular labral tears in patients presenting with hip or groin pain has been reported to be between 22% (Narvani et al., 2003) and 55% (McCarthy et al., 2001). There are few well-studied clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip labral tears. As the differential diagnosis for hip pain is broad, accurate clinical examination is important in guiding advanced imaging and identifying patients who may benefit from surgical management. Purpose:
A PT, an OS, and two ORs independently performed history and examinations with the emphasis of diagnosis on the results of six special tests. Results: Thirty-two of 37 individuals (86%) had labral tears to the hip at arthroscopy.
Information regarding acetabular labral tears and their association to capsular laxity, femoral acetabular impingement (FAI), dysplasia of the acetabulum, and chondral lesions is emerging. Specific provocative tests for acetabular labral tears have been described in the literature, all of which involve stressing or loading the hip joint in rotation. However, no single test has been identified as having a significant positive predictive value in .
wpi pipette
acetabular labrum hip surgery
An autoclave is a vital tool in scientific and medical laboratories, essential for ensuring the sterility of equipment and materials. Understanding its definition, principle of operation, key components, and operating procedures .
acetabular labral tear special tests accuracy trial|acetabular labral tear management